Nature-based solutions (NbS) involve working with nature to mitigate and resolve societal challenges, providing human well-being and biodiversity benefits. The UN Environment Assembly resolution has defined nature-based solutions as “actions to protect, converse, restore, sustainably use and manage natural or modified terrestrial, freshwater, a coastal and marine ecosystem which address social, economic and environmental challenges effectively and adaptively, while simultaneously providing human well-being, ecosystem services, resilience and biodiversity benefits.
Nature based solutions have the ability to mitigate the climate change issues. Addressing the climate and biodiversity crises requires immediate and sustained action to reach net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by mid-century. The transition to clean energy is necessary, but not sufficient, to achieve national and global climate goals.
Challenges Addressed by NbS
Reforestation /Afforestation to Sequester Carbon and Build Resilience
Pakistan is contributing only 1% to the global carbon emission. However, it is considered as one of the worst-hit climate change countries. As per the Bloomberg estimate only 5% of the country has been covered by the forest, against a global average of 31%., which is making it sixth most susceptible to climate change. The government has made efforts to protect the forest in the northern region of Khybe Pakhtunkhawa. Pakistan left with forest area of only 2% of the total land area, due to years of deforestation in 2020.
A billion trees planted in the KPK province are positively affecting the environment. It was estimated that it provides around $121 million of the economic benefit to the city in terms of carbon sequestration, watershed improvement and sustainable forest resources. The Nature based solution has the capacity to provide benefit by developing climate change adaptation, improving risk management and resilience, developing climate change mitigation, carbon sequestration, and increasing biodiversity (Nature , 2020).
Climate Change Adoption and Mitigation
It is one of the major challenges of developing countries. NbS in the form of ecosystem-based mitigation may have significant impact to fight against climate change and prevent environmental degradation and loss of natural ecosystems. It is found that degradation and deforestation contributes to carbon emission of around 4.4 Gigatonne (Gt) per year into the atmosphere. Nonetheless, the land sector including forestry, agriculture, and other land uses as a whole is emitting 24% of annual global anthropogenic emission. This emission can be reduced by following better conversion and land management practices. NbS can protect, strengthen the ecosystem and provide opportunities to address the current challenges and protect human well-being in the climate change events and its negative impact such as occurrence of extreme events, heat waves, floods (Mattews & Noordwijk, 2014).
Disaster Risk Reduction
Nature plays an important role to mitigate the risk related to disasters. The regulatory role of ecosystem service can provide cost effective solutions to combat risk. It is evident from the past that a natural hazard event has the potential to turn into a disaster, if the community or society is not able to cope with the impacts using its own resources. The Ecosystem Disaster Risk management system can have the ability to protect the environment by building break walls and sea walls. NbS has the ability to make the cities and human settlements safe and resilient and to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
Food Security
The word food security is defined as availability of food that is accessible to all, safe and locally appropriate and reliable through time and across space (IUCN, 2013). The NbS has potential to provide the solution and address the issues related to the food insecurity. These include protecting wild genetic resources (animal and plant), managing wild species (especially fish) and providing irrigation water. Moreover, by focusing on conservation, restoration and management of ecosystem will have ability to save the environment and help stabilisng the food access, availability and increase production. That can be used in the period of natural disaster, climate change and political instability.
Natural Regeneration to Address Biodiversity Loss
Nature based solutions have the attribute to address the climate and biodiversity crises. Investing in nature based solutions can help in protecting biodiversity. It includes different frameworks such as Forest Landscape Restoration (FLR), Ecosystem-based Adaptation (EbA) and Ecosystem-based Disaster Risk Reduction (Eco-DRR), and green infrastructures, contribute to the restoration, protection and strengthening of ecosystems they are implemented.
Increase Employment Opportunities
Nature based solutions provide and create employment opportunities for the people. ILO estimates that around 75 million people are already employed in NbS. It was predicted that 2 million jobs will be created by further harnessing the power of nature to mitigate the climate change challenge such as disaster risk, food and water insecurity. Majority of people working in occupations related to nature based solutions belong to Asian Pacific countries or lower income countries, although the majority of global NbS expenditure occurs in high income countries. Mostly people take it as a part time job.
In lower and middle income countries NbS mostly performed in the agriculture and forestry sector. In industrialised countries, where NbS spending where agricultural productivity is high, NbS spending is concentrated in ecosystem restoration and natural resource management. Public services contribute the largest share of NbS work in high income countries (37 per cent), with construction also representing a fair share (14 per cent). Few countries have introduced projects to support NbS and generate employment such as Public Employment Programmes (PEP) like India has introduced Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) and China’s has initiate Sloping Land Conversion Programme (Norton et al., 2020).
How Nature Based Solution Addresses the Problems?
There are several challenges that nature-based solution could address, such as:
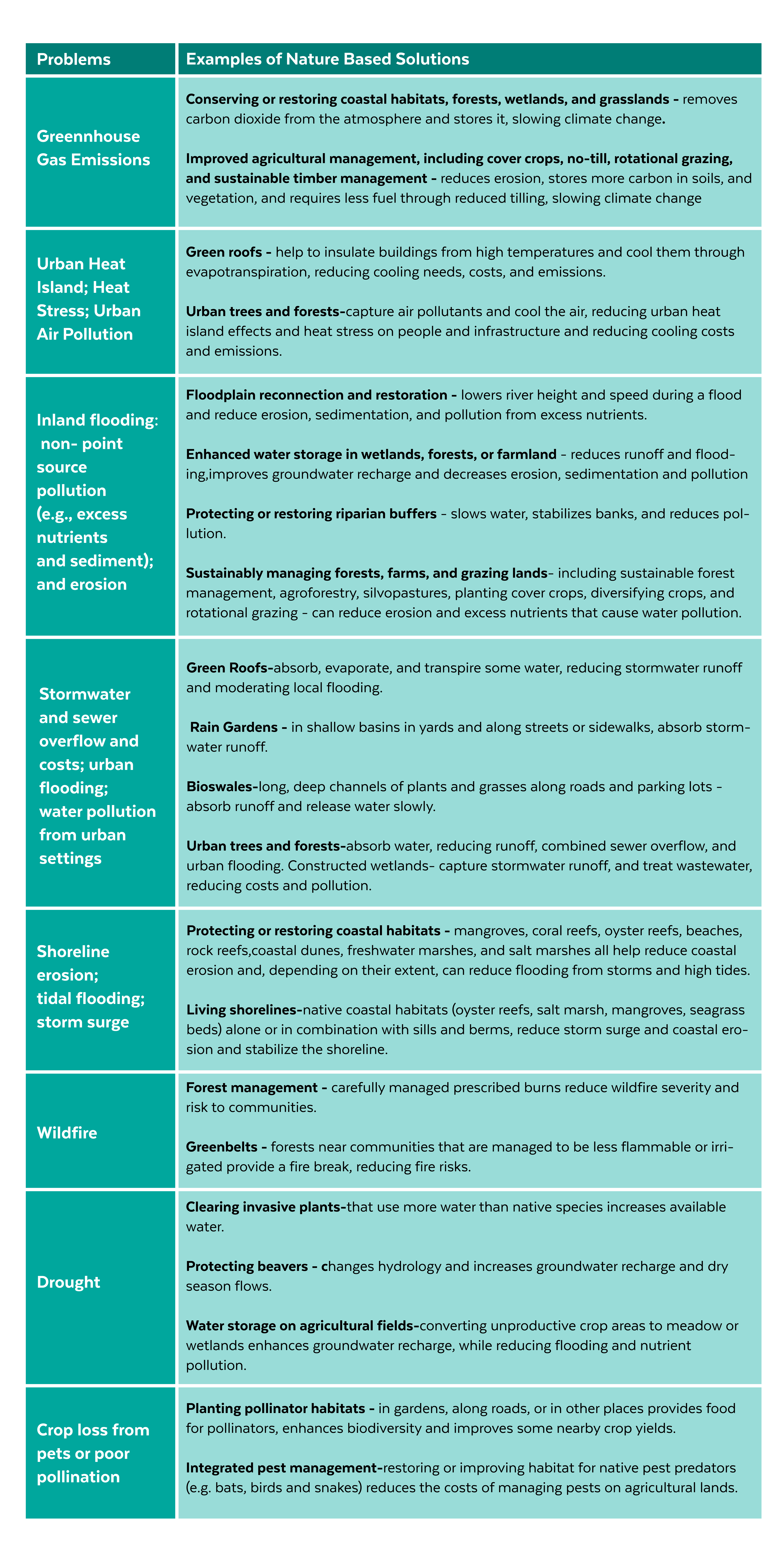
Source: National Climate Task Force
Conclusion
It is time for the environment sector and the development sector to move away from the perspectives that separate people from nature. Human actions of land/seascape do not only have environmental impact but economic, social and cultural impacts too. Conservation is a development issue and NbS are solutions that address multiple challenges such as forest degradation, food security, climate change and mitigation, address biodiversity loss, and other environmental issues.
This article is written by Sehrish Irfan. Sehrish is a Research Analyst at the Iqbal Institute of Policy Studies (IIPS).
References
IUCN. (2013). Food security policies: making the ecosystem connections. Retrieved from IUCN: https://www.iucn.org/downloads/iucn_food_security_en.pdf
Mattews, A., & Noordwijk, V. (2014). From euphoria to reality on efforts to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation (REDD+). Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change.
Network , N. (2020). A green wave of reforestation. Retrieved from Network nature: https://networknature.eu/casestudy/22707
Norton et al. (2020). Harnessing Employment-Based Social Assistance Programmes to Scale Up Nature-Based Climate Action. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.



Leave a Reply